配置并初始化一个仓库(repository)
开始或听着跟踪(track)文件
暂存(stage)或提交(commit)更改
配置Git来忽略指定的文件和文件模式
撤销错误操作
浏览历史版本以及不同提交间的差异
向远程仓库推送(push)
从远程仓库拉取(pull)文件
创建版本库
创建目录mygit1
$ mkdir mygit
进入mygit1
$ cd mygit
仓库初始化1
$ git init
Windows 系统下,通过Git Bash 操作如下: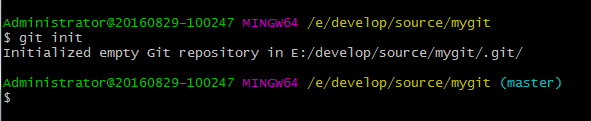
Mac 下,通过 Terminal 操作如下:
当执行完git init 命令后,可以看到控制台多出了(master)的标识,
它表示当前是在master分支,这也是 Git 为我们创建的默认分支(后面会详细介绍 Git 分支)。
使用ls -al 命令查看git init 命令为我们生成了哪些隐藏文件1
$ ls -al
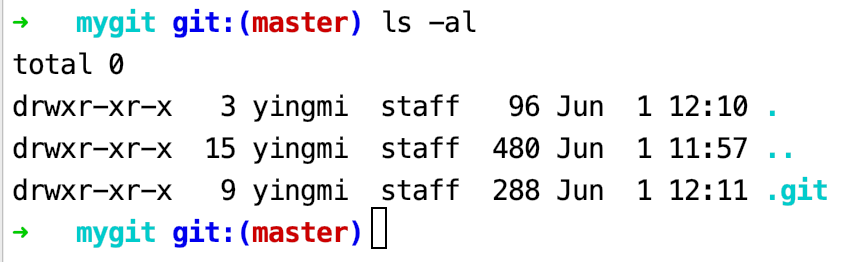
可以看到,mygit 目录下多出了.git 目录,这个子目录包含初始化的 Git 仓库所有必须的文件,
比如有我们在上一篇文章中介绍的关于git config –local配置方式中提到的config文件。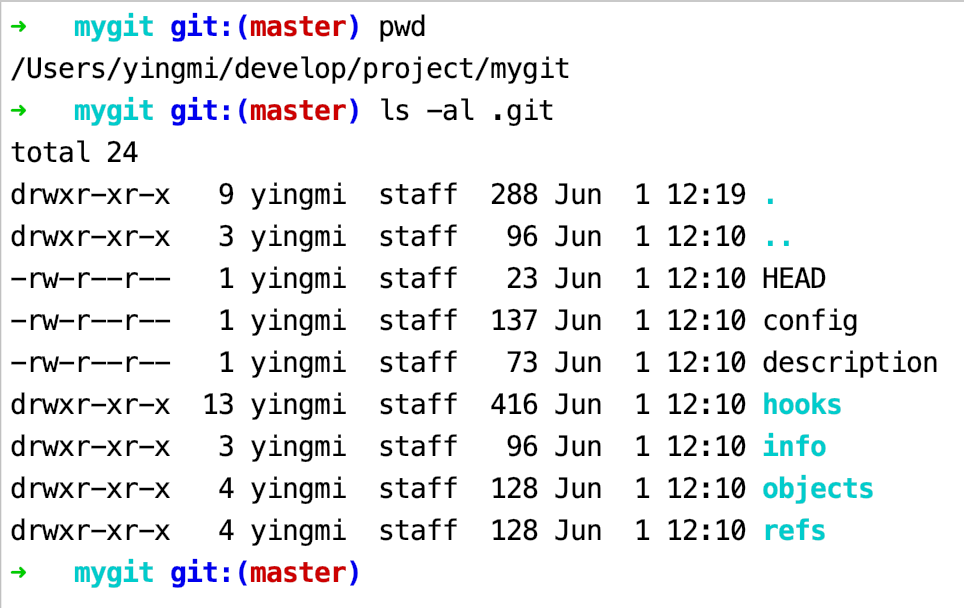
一般我们不会直接修改这个文件,而是通过Git 提供的命令去操作。
查看工作目录状态1
$ git status
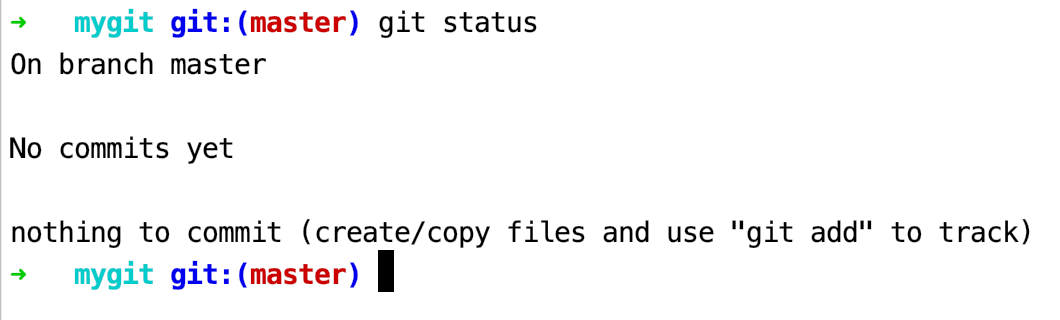
git status 命令将会成为以后经常会使用的命令,用来查看工作目录文件的状态,以便决定下一步的操作。
现在我们可以创建一个文件,然后使用git add 命令来实现对文件对追踪。1
$ touch hello.txt
编辑文件,添加如下内容1
vi hello.txt
1 | hello Git |
查看工作目录状态1
git status

在状态报告中可以看到,当前在 master 分支,hello.txt 文件未被跟踪,
我们可以使用 git add 命令来实现对文件的跟踪。
开始跟踪hello.txt文件1
$ git add hello.txt

控制台没有任何信息输出(Linux/Unix系统的设计思想:没有消息就是最好的消息)
也可以使用git add . 命令对当前目录下所有文件进行跟踪。
查看状态1
$ git status
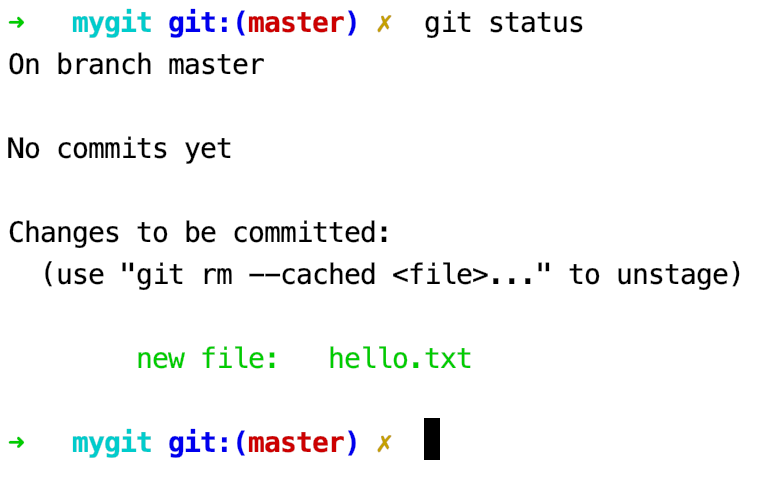
可以看到,hello.txt文件已被跟踪,并处于暂存状态,只要在Changes to be committed:这行下面的,就说明是已暂存状态。
对于已暂存的文件,我们可以将hello.txt文件从暂存区回退到工作区,也可以提交hello.txt文件。
这里我们先演示从暂存区回退到工作区1
$ git rm --cached hello.txt

查看状态,发现和刚创建完文件时一样。
接下来,我们重新将hello.txt 文件添加到暂存区1
$ git add hello.txt
提交到版本库1
$ git commit
输入git commit直接回车,默认会调用本机文本编辑器,需要输入提交信息,我们输入commit hello.txt信息,保存,关闭文件。
Windows 系统下,通过Git Bash 操作如下: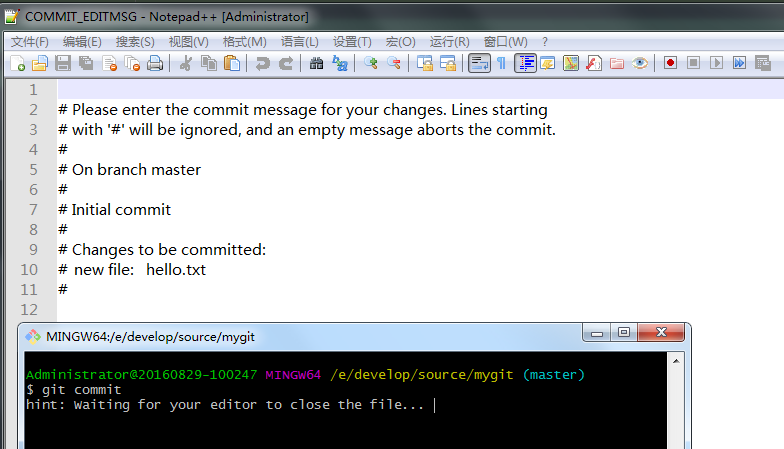
Mac 下,通过 Terminal 操作如下:
此时,hello.txt文件已成功提交,可以看到如下信息: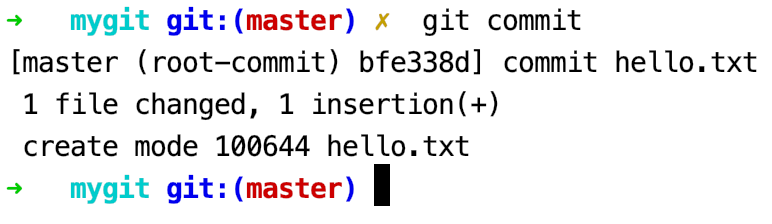
一般情况下,我们输入的提交信息都不会特别多,这时我们可以使用 git commit -m "提交信息"。
查看工作区状态1
2
3$ git status
On branch master
nothing to commit, working tree clean
说明现在的工作目录很干净。换句话说,就是当前目录下没有出现任何未跟踪状态的新文件,
并且所有已跟踪文件在上次提交后都没有被修改过,否则Git 会在这里列出来。
查看提交日志1
$ git log
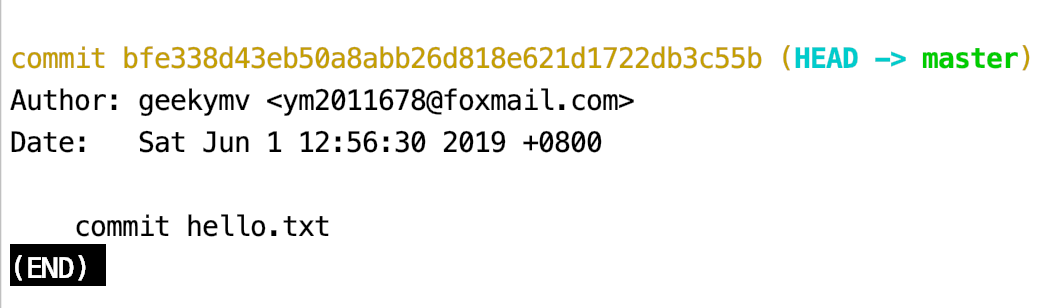
默认不加任何参数的话,git log 会按提交时间列出所有的更新,最近的更新排在最上面。
git log 命令会列出每个提交的SHA-1 校验和、作者的名字和电子邮件地址、提交时间以及提交说明。
暂存修改的文件
修改hello.txt 文件1
$ vi hello.txt
内容如下:1
2hello Git
hello Java
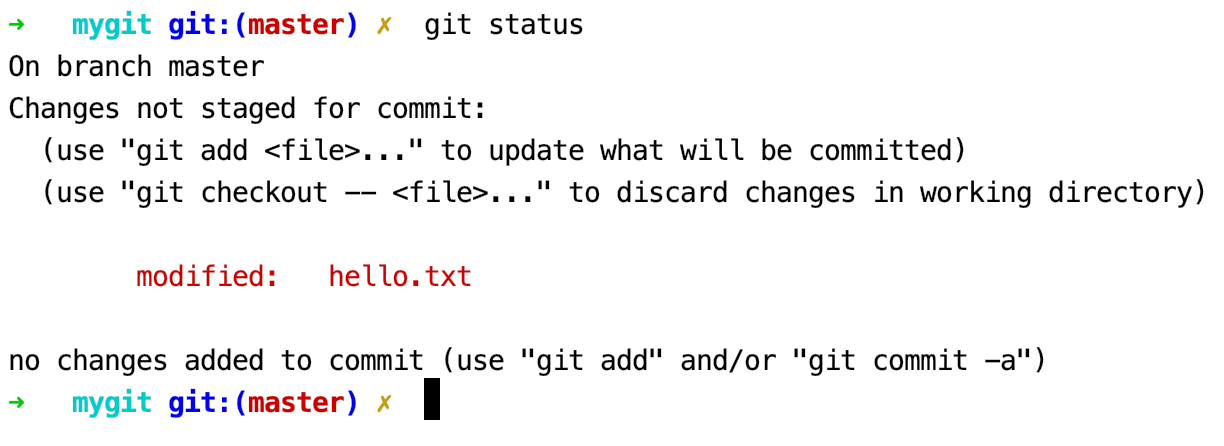
出现在Changes not staged for commit 这行下面,说明修改了已跟踪的文件,但还没有放到暂存区。
要暂存这次更新,需要运行git add命令。或者使用git checkout 命令将工作区的文件撤销修改。git add 是个多功能的命令:
- 用于开始跟踪新文件;
- 把已跟踪的文件放到暂存区;
- 用于把有冲突的文件标记为已解决状态(这个后面会用到)。
我们先演示下使用git checkout 命令撤销修改1
git checkout -- hello.txt
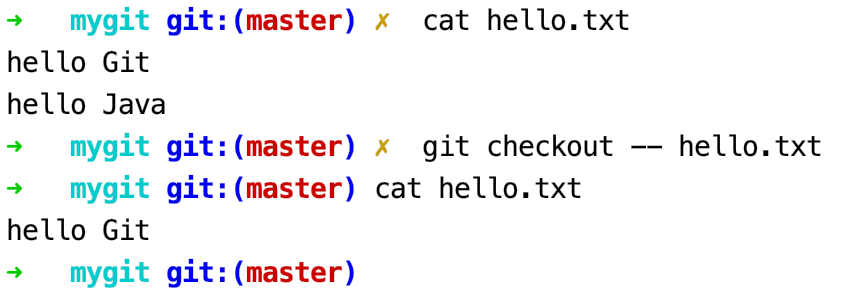
可以看到hello.txt文件中添加的一行文本(hello Java)被撤销。
我们按照上面的方式再修改hello.txt文件,演示将修改添加到暂存取的功能
运行git add 命令将已修改的hello.txt 文件放到暂存区1
$ git add hello.txt
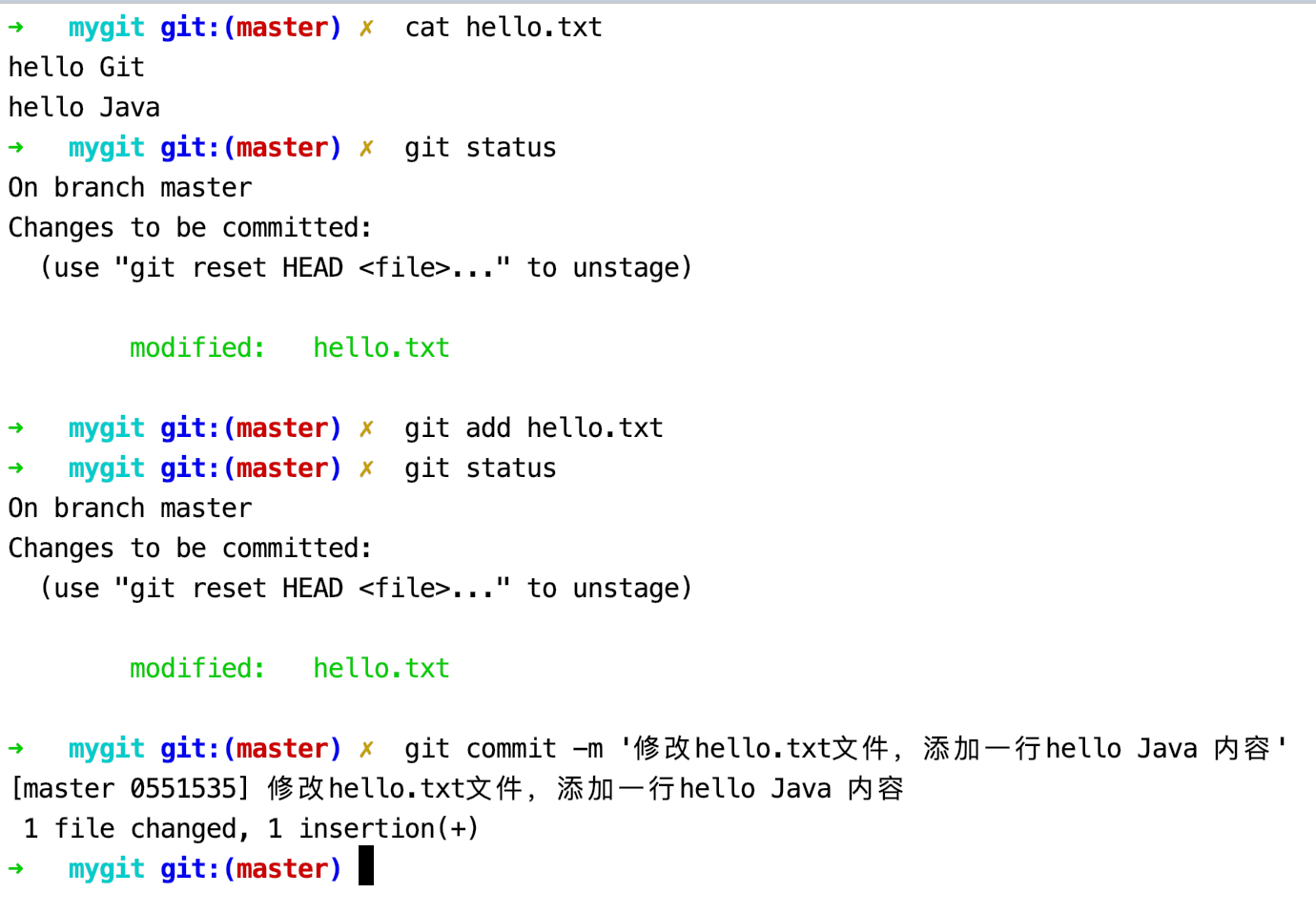
通过git status 可以看到hello.txt文件的修改已暂存。
状态简览
git status 命令的输出十分详细,使用 git status -s 或 git status --short 命令可以得到更为紧凑的格式输出。1
git status -s
新添加的未跟踪文件前面有 ?? 标记
新添加到暂存区的文件前面有 A 标记
修改过的文件前面有 M 标记,注意M有两个可以出现的位置,
出现在右边的M表示该文件被修改了但还没有放到暂存区,出现在左边的 M 表示该文件被修改并放入了暂存区。
查看已暂存和未暂存的修改
1 | git diff |
git diff 不加任何参数比较工作目录中的当前文件和暂存区之间的差异
git diff HEAD 比较工作区与最新本地版本库
git diff commit-id 比较工作区与指定 commit-id 之间的差异
git diff –cached 比较暂存区与最新本地版本库
git diff –cached commit-id 比较暂存区与指定commit-id 之间差异
提交时跳过使用暂存区
git commit 使用暂存区可以精心准备要提交的内容,但有时候这么做略显繁琐。Git提供了一个跳过使用暂存区的方式,
在提交的时候给git commit 加上-a 选项,Git会自动把所有已跟踪过的文件暂存起来一并提交。1
git commit -am '提交说明'
移除文件
要从Git中移除某个文件,就必须要从已跟踪文件清单中移除,然后提交。1
2git rm hello.txt
git commit -m '提交说明'
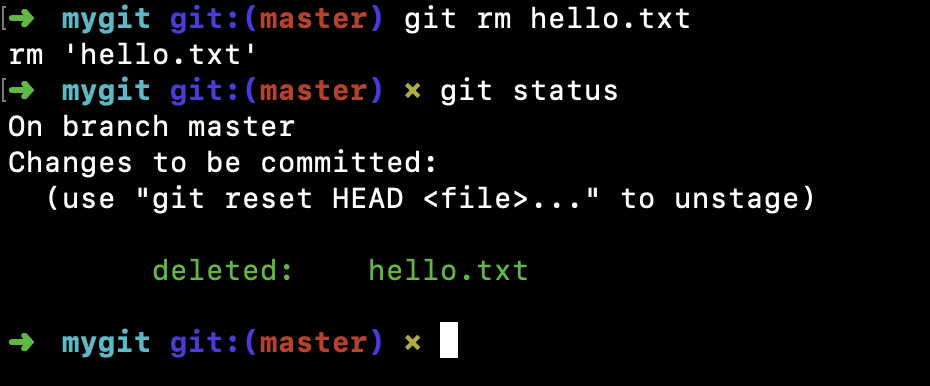
大部分情况下,我们会直接在文件管理器中把文件删除了或者使用rm 命令删除1
$ rm hello.txt
1 | $ git status |
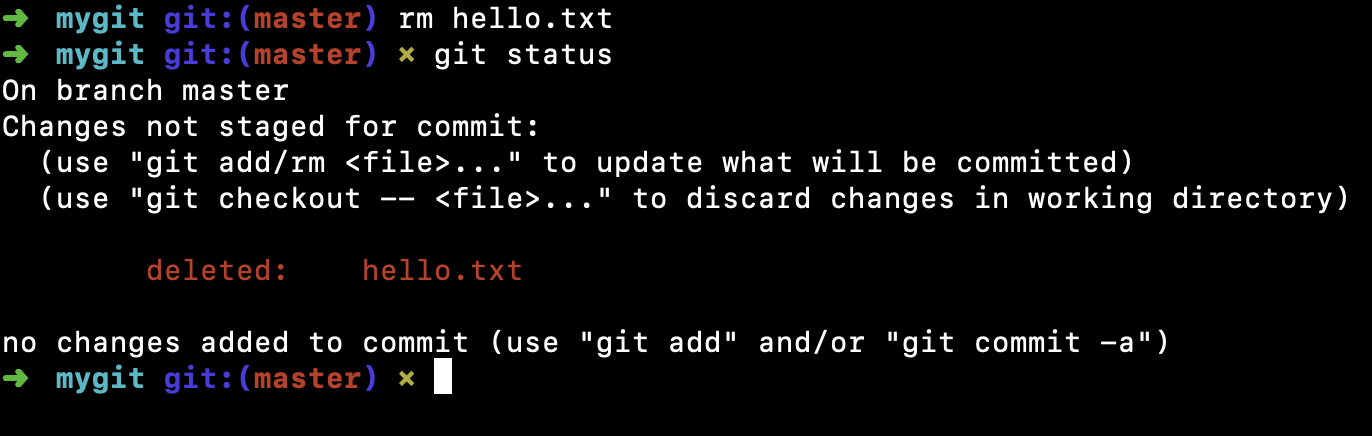
有两个选择:
1.确实要从版本库中删除该文件,就用git rm 记录此次删除文件的操作,并用git commit。1
2git rm hello.txt
git commit -m '提交说明'
现在文件就从版本库中删除了。
2.删错了,把误删的文件恢复到最新版本。1
git checkout -- hello.txt
用版本库里的版本替换工作区的版本,可能会丢失最近一次提交后你修改的内容。
想把文件从Git仓库中删除,但是仍希望保留到当前工作目录中,
git rm –cached hello.txt
重命名文件
在我们日常开发中,可能会出现修改文件名的情况,比如觉得某个类的名字取的不能够见名知义,想要修改。
要在Git 中对文件重命名,可以使用git mv 命令1
$ git mv file_from file_to
比如,我们将文件 hello.txt 改名为hello2.txt1
$ git mv hello.txt hello2.txt
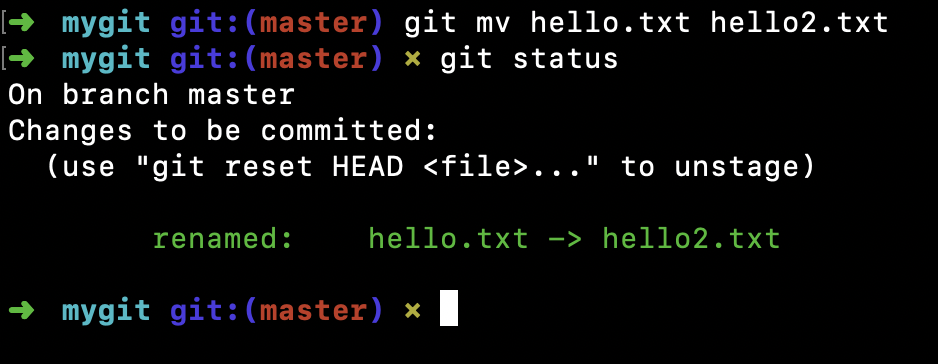
查看状态信息,可以看到 Git 能够识别到我们对文件执行了重命名操作,并且已是暂存状态。
运行git mv 相当与运行了下面三条命令:1
2
3$ mv hello.txt hello2.txt
$ git rm hello.txt
$ git add hello2.txt
重命名已完成,这个时候我们可以提交修改 git commit -m "重命名文件"。
或者误操作了这个文件,想要回退。1
$ git reset HEAD hello2.txt
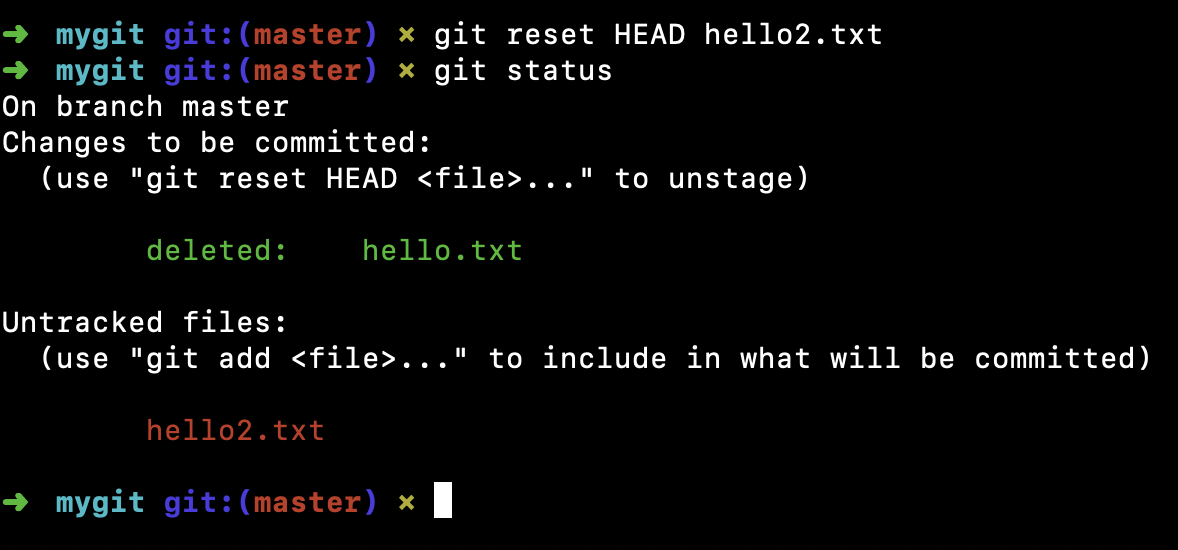
这样hello2.txt 文件处于未跟踪状态了。
1 | $ git reset HEAD hello.txt |
1 | $ git checkout -- hello.txt |
文件撤销
在日常开发的过程中,我们可能会遇到以下几种的场景:
场景一:
在工作区修改了文件内容,还没添加到暂存区,发现修改错了想要撤销修改。1
2$ cat hello.txt
hello Git
修改hello.txt 文件,添加一行内容hello world1
2
3$ vim hello.txt
hello Git
hello world
1 | $ git status |
使用git checkout -- <file>... 撤销修改1
$ git checkout -- hello.txt
查看状态1
2
3$ git status
On branch master
nothing to commit, working tree clean
查看hello.txt 文件内容1
2$ cat hello.txt
hello Git
hello.txt 文件回到和版本库一样。
场景二:
与场景一一样在工作区修改了文件内容,不同的是这个时候被修改的 hello.txt 文件已经添加到暂存区了,需要撤销修改。1
2
3$ vim hello.txt
hello Git
hello world
查看状态1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9$ git status
On branch master
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: hello.txt
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
将修改的文件添加到暂存区1
$ git add hello.txt
查看状态1
2
3
4
5
6$ git status
On branch master
Changes to be committed:
(use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
modified: hello.txt
现在我们首先将文件从暂存区回退到工作区1
2
3$ git reset HEAD hello.txt
Unstaged changes after reset:
M hello.txt
查看状态,此时和场景一的状态是一样的了。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9$ git status
On branch master
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: hello.txt
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
使用git checkout -- <file>... 撤销修改1
$ git checkout -- hello.txt
场景三:
与场景二一样在工作区修改了文件内容,被修改的 hello.txt 文件已经添加到暂存区了,这个时候在工作区又做了修改,需要撤销本次修改。
1 | $ vim hello.txt |
将修改的文件添加到暂存区1
$ git add hello.txt
再次编辑文件,添加新的一行内容hello Java1
2
3
4$ vim hello.txt
hello Git
hello world
hello Java
查看状态1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12$ git status
On branch master
Changes to be committed:
(use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
modified: hello.txt
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: hello.txt
此时,hello.txt 文件同时出现在暂存区和非暂存区。
我们想要撤销本次的修改,那么只要执行git checkout -- hello.txt 就可以了。1
2$ git checkout hello.txt
Updated 1 path from the index
1 | $ git status |
查看文件内容,本次修改已经撤销了。1
2
3$ cat hello.txt
hello Git
hello world
文件撤销小结
如果hello.txt 修改后,还没有添加到暂存区,现在想要撤销,执行git checkout -- hello.txt 则回到和版本库一样的状态。
如果hello.txt 已经添加到暂存区,又做了修改,现在想要撤销本次修改,执行git checkout -- hello.txt ,撤销的是工作目录的修改,则回到和暂存区一样的状态。
当然如果是一个新的文件还没有添加到暂存区,也就没有Git撤销操作了。总之,就是让这个文件回到最近一次git commit或git add时的状态。
场景四:
这个时候终于把hello.txt 文件修改完了,愉快的执行了提交。1
2
3$ git commit -m "fix bug #666"
[master 50b27fc] fix bug #666
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
提交完后发现bug号写错了,其实修改的是bug #66,想要修改提交说明。
查看提交说明1
2
3
4
5
6
7$ git log
commit 50b27fce9b19dd25736893bcc3bb49c46a1242ae (HEAD -> master)
Author: geekymv <[email protected]>
Date: Thu Jun 13 19:22:14 2019 +0800
fix bug #666
修改最近一次的提交说明1
2
3
4
5$ git commit --amend -m "fix bug #66"
[master 5c10da1] fix bug #66
Date: Thu Jun 13 19:22:14 2019 +0800
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
1 | $ git log |
已经成功修改了提交说明,并没有新增commit id。
版本回退
1 | $ git log |
git log 命令显示从最近到最远的提交说明,如果觉得输出的信息太多,可以加上参数--pretty=oneline1
2
3
4$ git log --pretty=oneline
5c10da1d45b53cf2f98c538b9f8d758ff961fd81 (HEAD -> master) fix bug #66
29cf508b469fd4b89de66b8b979e14b10c2663ea 修改文件
0a49afaf82d809568ecc942baf4c170d5027ef6d add
这下清爽多了!
在Git中,用HEAD表示当前版本,上一个版本就是HEAD^,上上一个版本就是HEAD^^,
当然往上10个版本写10个^比较容易数不过来,所以写成HEAD~10。1
2$ git reset --hard HEAD^
HEAD is now at 29cf508 修改文件
1 | $ git log --pretty=oneline |
可以看到当前版本是29cf50...。
现在要想还回到指定回到5c10da1d45b53cf2f98c538b9f8d758ff961fd81版本,
当然版本号没必要写全,前几位就可以了,Git会自动去找。
1 | $ git reset --hard 5c10da |
可以看到又回到了5c10da...版本1
2
3
4$ git log --pretty=oneline
5c10da1d45b53cf2f98c538b9f8d758ff961fd81 (HEAD -> master) fix bug #66
29cf508b469fd4b89de66b8b979e14b10c2663ea 修改文件
0a49afaf82d809568ecc942baf4c170d5027ef6d add
当你用$ git reset --hard HEAD^命令回退到29cf50...版本时,再想恢复到最新版本怎么版呢?
上面我们能恢复是因为我们在笔记中记录了 commit id。这个时候使用git log 已经看不到最新版本到commit id 了。
不用担心,在Git中总是有后悔药可以吃,git reflog记录你的每一次命令。1
2
3
4
5
6$ git reflog
29cf508 (HEAD -> master) HEAD@{0}: reset: moving to 29cf
5c10da1 HEAD@{1}: reset: moving to 5c10da1d45b53cf2f98c538b9f8d758ff961fd81
29cf508 (HEAD -> master) HEAD@{2}: reset: moving to HEAD^
5c10da1 HEAD@{3}: commit (amend): fix bug #66
50b27fc HEAD@{4}: commit: fix bug #666
